
Some examples below detail the different types and complexities of exception rules. Most users simply add an exception rule for a specific program and let that program decide which ports it needs using UPnP.
You can make exception rules for any program running on your computer, any single port ranging from 1 to 65535, or a port range like 6881 to 6889. This exception rule can have very specific rules, or quite relaxed rules, depending on your needs.
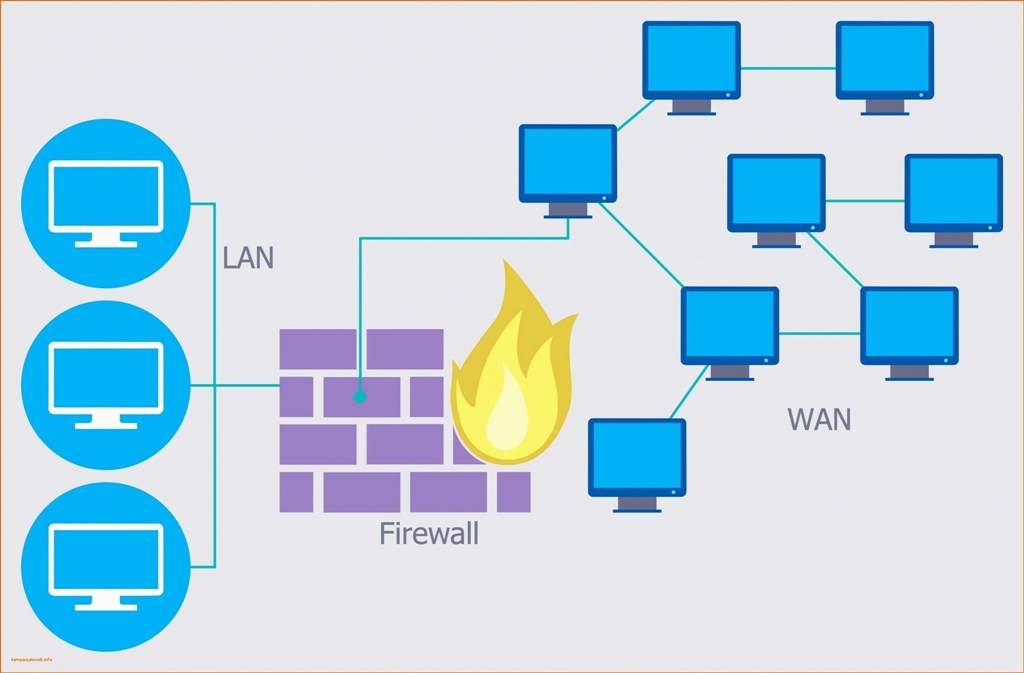
The only way data can pass to and from your computer is if you add an exception rule, or a “bridge over the moat”. Try to think of a firewall like a moat around your computer, and an exception rule like a bridge over the moat. Larger corporate networks generally use a dedicated hardware firewall.

Firewalls generally block all traffic (data transfer) unless a specific rule/exception is added to allow traffic to pass. A computer Network Firewall is either: (1) a software program installed on your PC (2) a built-in firewall inside your modem or (3) a dedicated hardware firewall.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
